
Monika Vidak
University of Zagreb, Croatia
Title: Protein content in common bean row seeds in relation to a* and b* dimensions of the L*a*b* color space
Biography
Biography: Monika Vidak
Abstract
Although production of common bean in Croatia is in decline, it is very important grain legume in human consumption because of high nutritional value. The production is based on landraces which are adapted to local environments. The aim of this study was to quantify the protein content on 226 common bean accessions and to investigate the relationship between seed coat color and protein content of landraces as part of the Croatian Science Foundation project "Genetic basis of bioactive nutrient content in Croatian common bean landraces". Seeds of accessions belonging to five most widely used landraces named 'Biser', 'Kukuruzar', 'Puter', 'Trešnjevac' (2 - climbing and 3 - determinate bush) and 'ZelenÄec' were assessed. The L*a*b* values were measured in order to describe the seed coat color. Results show that accessions that have higher a* (red – green) and b* (yellow – blue) values tend to have higher crude protein content. Considering that protein content is generally considered as a very important trait to estimate the nutritional quality of common bean seeds, 'Trešnjevac' 2 would be of an interest for breeding purposes due to the highest protein content.
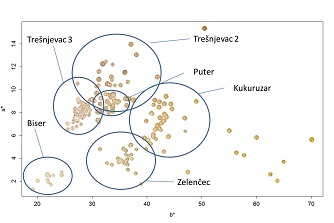
Figure 1. Protein content of Croatian landraces in relation to the different seed coat color

